Personal Pages
Gusti Ahmad Fanshuri Alfarisy, Ph.D.
from world import netizens
print("Hello world!")
print("Greetings from Borneo Islands...!")

Research Agendas

We have experienced the outstanding performance of artificial intelligence surpassing human capability. Yet, they are unable to acknowledge fully that they do not know and learn the novel phenomenon continuously like humans. In my current research agenda, I am exploring a technique to enhance an agent to identify unknown categories and learn them continuously in domain-specific problem. This will make the agent become reliable and able to adapt to the open-world environment in the agent interest only. The applications can be applied to ecology, healthcare, smart cities, robotics, chatbot or intelligent systems. We named this as Domain-Specific Open-World Recognition.
We are interested in the domain-specific open-world recognition problems in Environmental/Biodiversity Monitoring and Conservation, Lifelong Chatbot, AI-generated content detection, and Agriculture/Food.
Short Biography
Hi, greetings from Borneo Island! I am an assistant professor at Institut Teknologi Kalimantan at the Department of Informatics. I have been teaching several topics including algorithms and programming languages, data structures, functional programming, numerical methods, machine learning, artificial intelligence, deep learning, web intelligence, and software engineering. I have reviewed several articles in Springer and Elsevier Journals. My research interest includes:
- Open-World Lifelong Machine Learning (OWLML)
- Ecological and Environmental Informatics
- AI Generated Content (AIGC) Detection System
- Chatbot with OWLML
Main Projects
Open-World Lifelong Learning for Biodiversity Monitoring
In a world teeming with diverse ecosystems, continuous and adaptive biodiversity monitoring is vital, as biodiversity plays a crucial role in our sustainability as humans. Open-world lifelong learning offers an innovative approach to monitoring that evolves alongside the environment. Unlike traditional models, which require retraining with new data and struggle to identify unknown classes, open-world lifelong learning systems autonomously learn and adapt over time, recognizing and integrating new species and ecological changes without restarting from scratch. The primary challenge lies in mitigating catastrophic interference to achieve true open-world capability.
Ongoing:
- Open-Set Plant Species Recognition with Continual Learning
- Active Learning Strategies for Plant Species Classification
- An Integrated Biodiversity and Forestry Portal for Borneo
- Large-Scale Open-Set Plant-Species Recognition using Lightweight Deep-Learning Models
Open-World Detection of LLM-Generated Content
With the rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs), an increasing amount of AI-generated and potentially misleading content has emerged online. As LLMs continuously evolve and improve their generalization capabilities, detecting machine-generated content becomes increasingly challenging in dynamic and open environments. This project aims to address this issue by leveraging open-world and lifelong learning approaches to develop adaptive detection systems capable of identifying LLM-generated content under continuously changing conditions.
Ongoing:
- Open-Set Recognition for AI-Generated Image Detection
Final Exam Information (Introduction to Artificial Intelligence)
December 05, 2025

Lecture Notes 5: Logical Agent and First-Order Logic
October 01, 2025

Lecture Notes 6: Python Itertools and Functools
September 24, 2025

Lecture Notes 4: Adversarial Search and Games
September 22, 2025

Lecture Notes 4: Recursion and Y-Combinator
September 18, 2025
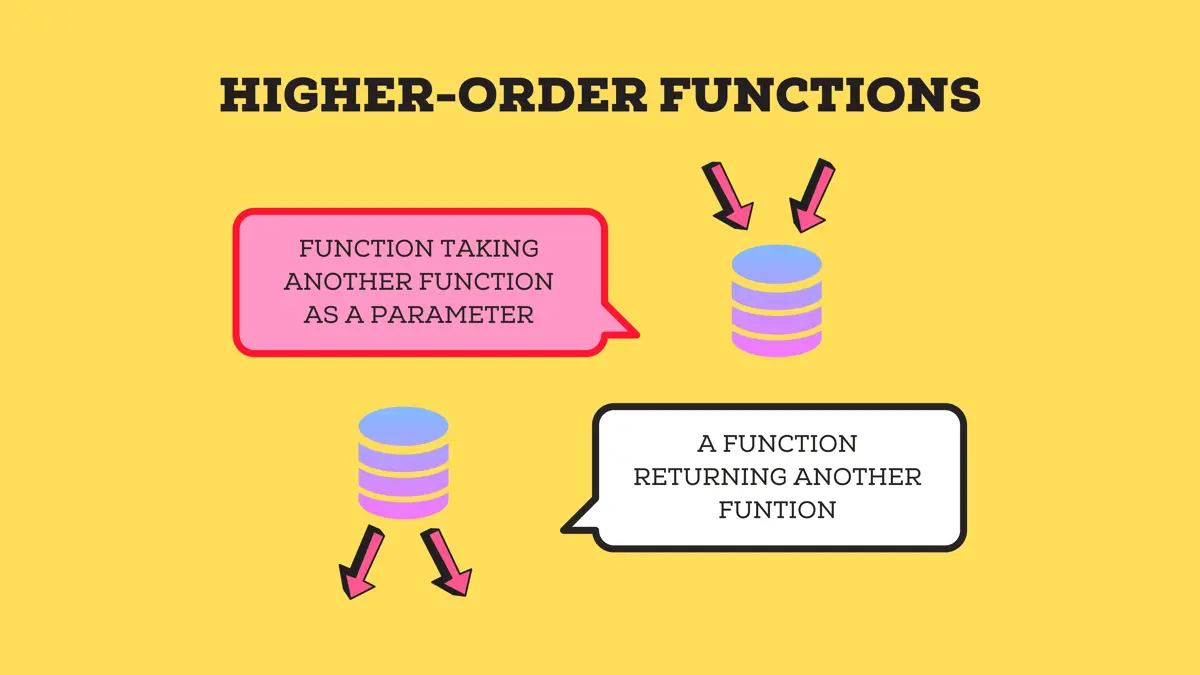

_03400068.png)
